“Beneath the white bark of the birch, a symbol of resilience and renewal, lies the wisdom of a forest that teaches those who know how to listen.”
Axel Lagardere
Birch bark is an excellent natural fire starter due to several of its unique properties:
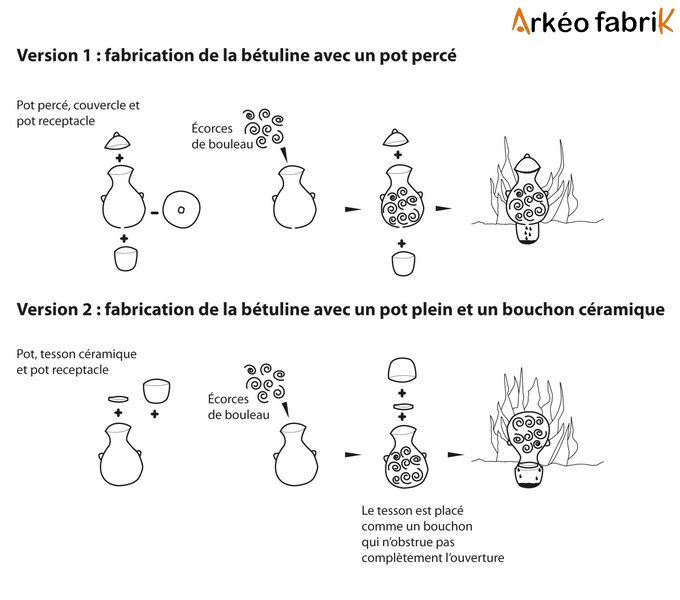
Riche en huiles volatiles (bétuline)
The bark of the birch tree contains a naturally flammable oil called Betulin. This oil allows for easy burning even when it is slightly damp.
Betulin is a stable substance that does not degrade quickly over time as long as you protect the bark from moisture in the long term and from prolonged exposure to sunlight and very dry air, which can more rapidly alter the volatile oils.
Texture fibreuse et fine
The layers of birch bark are thin, lightweight, and easy to tear, which increases the surface exposed to fire and thus helps the flames spread quickly.
Imperméabilité naturelle
The bark of birch is resistant to moisture due to its waxy composition. It remains flammable even after exposure to water, making it a reliable choice in a humid environment.

The bark of the birch tree also has good physical, medicinal properties, and is practical for survival:
Pour la fabrication :
With its waxy compounds, it can be used as a sealing material, for example, to make containers or cover a shelter.
When it is fresh, birch bark is flexible, making it ideal for the production of baskets or canoes, etc. Once dry, it becomes rigid and durable.
Thanks to its multilayer structure, the bark acts as an excellent insulator against cold or heat and can be particularly used to line shelters.
By heating the bark, a sticky resin can be extracted that is traditionally used as a natural glue for repairing objects or assembling tools.
Pour ses propriétés médicinales ou nourrissante :
Betulin and other compounds present in the bark have antimicrobial properties; it was traditionally used to disinfect wounds (antiseptic) or treat skin inflammations. It can also accelerate healing due to its soothing and protective properties. Birch bark helps prevent fungal infections, which is useful in a humid environment.
The tannins found in the bark are useful for treating animal hides (tanning) but especially for purifying water due to their astringent properties.
The inner layers of the bark (the cambium) are indeed bitter but edible and rich in nutrients; they can be consumed fresh, boiled, dried, or ground into flour (be careful, harvesting the cambium from a tree can severely damage it, only eat it as a last resort).
The birch is a living being, so prioritize those that are dead or on the ground before harvesting the bark of a living birch, as its bark serves to protect it from insects, diseases, and parasitic fungi; it also plays an important role in its ecosystem:
It provides shelter for wildlife such as birds and certain species of insects, and by naturally shedding, its bark helps enrich the soil with organic matter.

Thank you for reading this article, I hope you enjoyed it